Parametric wall with PARA 2

This is a new edition of old video tutorial (Parametric Brick wall) which uses link and math controllers to create a random pattern of stone blocks.
March 11, 2012 at 10:11 am Comments (0)

This is a new edition of old video tutorial (Parametric Brick wall) which uses link and math controllers to create a random pattern of stone blocks.

This video shows that random controller can produce Boolean values (TRUE-FALSE). For each object in the array Random controller returns True or False based on the user defined percentage. Higher value makes the controller to return True more often and lower value causes more False result.You can make decision based on the result of the random controller through a condition controller . This process is similar to coin flipping.
This video demonstrate a very simple and quick technique which uses the surf-deform modifier and PARA 3d to clad a NURBS surface, if you work on patches you may use patch deform instead. In second video you learn how to use offset controller and sub-object controllers to slide the hexagon shape panels on the surface in a way that they make a honeycomb pattern.
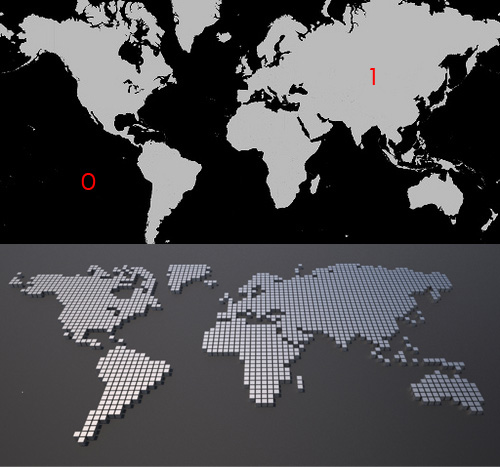
In this video we use collection controller to find the position of those points which they are located on white sections of an image. The image is being process by a bitmap controller and if the value is greater than .5 (gray) the test controller returns true. collection controller goes through the entire array of points and collects only the position of the points which meets our condition. to set the position of each box to the corresponding point in collection we use a list controller. list controller takes the index value (location of the box in the array) and return the same item from the collection.
We use curve controller in PARA 3D to visualize the curvature of a spline object.
In first video you learn how to find the intersection of two coplanar lines. Notice that if two lines are not intersecting program will generates some error. in the second video we find the closest point on one line to a series of lines from another parametric array. Program automatically sets the controllers for point A and B. if two lines are actually intersection the closest point is equal to the intersection point. also you can find the apparent intersection of two lines on a plane. For example the apparent intersection on XY plane is the intersection of projected lines on this plane(intersection from top view) .
In this video you learn how to use the Material modifier to control the material of the objects inside the array.
Here is a short video explaining what type of objects you can use in surface controller.
we can summaries all as following:
Also as a general rule, surface controller in 2d Arrays cannot be used on objects which have more than one smooth manifold (surface), for example a cylinder with top and bottom caps does not represent one surface while a cylinder (tube) without caps can be described as one single manifold.
In PARA 2.6 you can replace the items of the array with a new object with same modifier stack.
This video shows the procedure.
I was challenging the PARA II to model something like the Allianz Arena stadium in 3DS MAX. Each panel composed of a solid flat frame and a bulged part. To imitate the lighting effect I assigned a material modifier to the smooth part of panel and a Pattern controller change the index value.
The skew effect of the skin is the result of the deform controller that takes the initial value from the sub-object controller and pass it to the UVW offsets in surface controller. The disadvantage of this method is when you try to use the UVW mapping to get uniform subdivision all over the surface. I shall add an option to surface controller to fix this problem soon.